1. Introduction
Currently, internet and media platforms such as Facebook, Google and Yahoo collect user data free of cost, and sell it off to 3rd party vendors. Moreover, only big corporations have the means to execute big data tasks, as these companis possess both the expensive hardware and the consumer data. In today's world of decentralization, users should be able to completely own their data, and monetize it if they want to. DxChain is looking to mitigate the issues of data ownership, security and privacy by designing a platform to provide computation services related to big data and machine learning, using decentralized storage services. Their decentralized data exchange platform will enable users to completely own and trade their data.
2. Architecture Overview
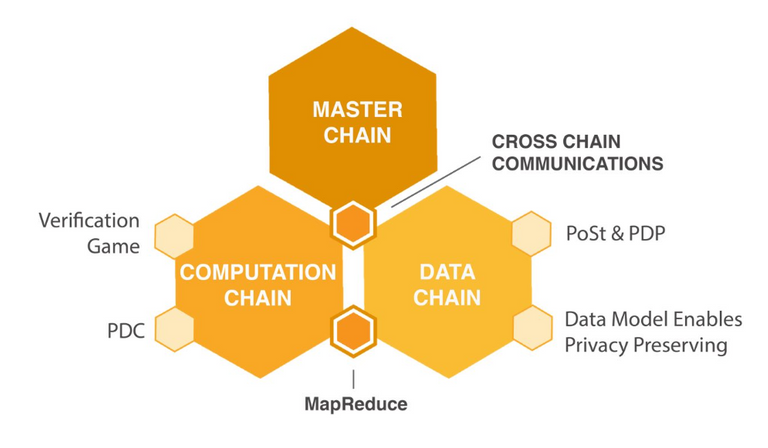
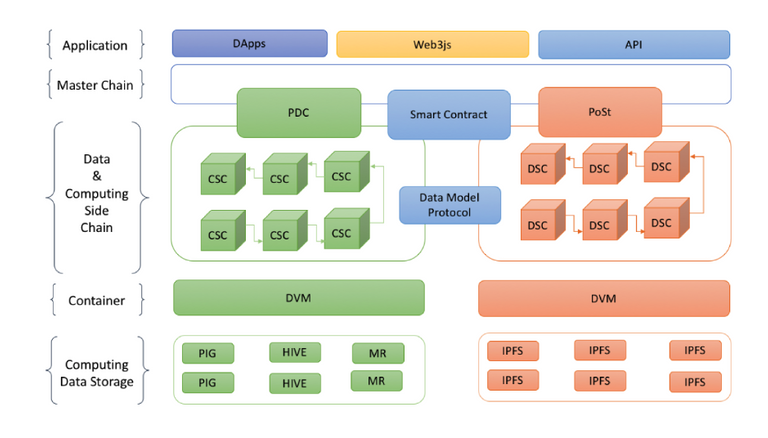
DxChain implements a chain-on-chain architecture, which comprises of a Master Chain, a Data Side Chain and a Computation Side Chain. The Master Chain is similar to traditional blockchains (like Bitcoin and Ethereum). It acts as the public ledger, and stores asset information and smart contracts. The Master Chain uses Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism for ensuring security of the network.
In order to make the solution scalability, DxChain introduces 2 sidechains – the Data Side Chain (DSC), which stores non-asset information, and the Computing Side Chain (CSC), which stores specific computing tasks. The sidechains communicate with the Master Chain through smart contracts, and improve the efficiency of data storage and computation. They use different consensus algorithms for maintaining network security.
3. Network Computations
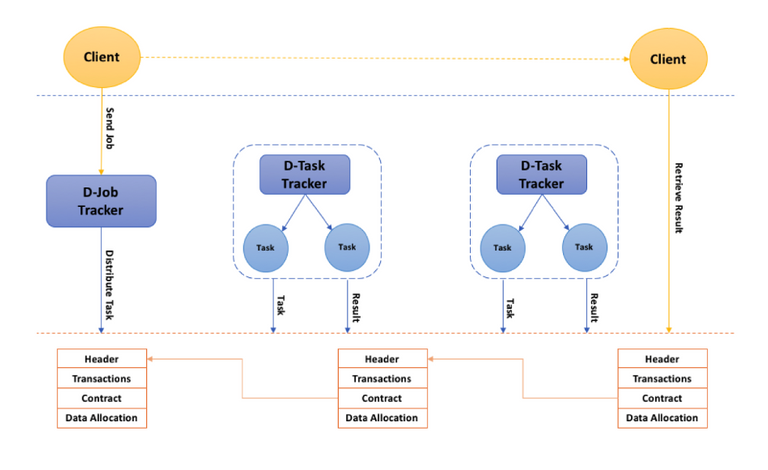
Computations running on Dxchain will support more general-purpose processing compared to just verifying transactions, such as database query and MapReduce. Dxchain uses 2 mechanisms to ensure correctness of computations – Verification Game Algorithm (VGA) and Provable Data Computation (PDC). Both these mechanisms are used by the network to ensure whether a computation procedure is correct using very low computational resources. This enables MapReduce algorithms to be executed on the DxChain platform.
A consensus algorithm called the Proof of Spacetime (PoSt) is used by the Data Side Chain. It allows users to verify the data stored on a server without retrieving it, and is extremely useful for remote data checking and cloud computing. The Computation Side Chain uses PDC mechanism for arriving at consensus.
4. Integration with Hadoop
Hadoop is a well-known distributed file storage and computation network. The Hadoop ecosystem comes with a huge collection of tools, such as Pig, Hive and Mahoot. The team at DxChain is working on developing DPig, DHive and DMahoot to improve the computations on the DxChain network. This is just the beginning, and the developers would be working on adapting more features from the Hadoop ecosystem to the DxChain network with time. As mentioned earlier, both the VGA and the PDC make it possible for MapReduce programs to be run on the DxChain ecosystem.
5. Final Word
DxChain is trying to adapt the Hadoop ecosystem to a decentralized environment. The white paper highlights numerous other applications too, such as smart city, health care, automated data sample collection and AI training. This is an extremely ambitious project, but they have the team with the required technical expertise to realize this vision. All of the core team members have more than 10 years’ worth of experience in fields of big data, blockchain, network security and distributed systems. As far as I know, no other project is working on this topic. Even if they achieve half of what they have set out to do, they will end up making a big impact in the worlds of both big data and blockchain.
Website: https://www.dxchain.com/
My referral link: https://t.me/DxChainBot?start=3yjg7x-3yjg7x

Congratulations @aaboltaabol! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!