The impact of planetary revolution as follows:
1. Changes in Day and Night
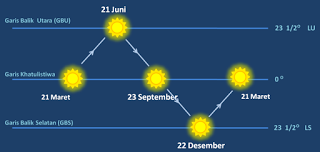
The sun does not rise from the same place, but shifts little by little. The shift of the rising sun points follows the orbit of the Sun. The position of the Sun shifts from the equator to the north-back line then to the southern line by passing the equator. After arriving at the south line, the position of the Sun shifts back again to the equator. The shift in the position of the Sun is caused by a combination of Earth's revolutions and the axis of Earth's axis to the plane of the ecliptic.
Sun's shimmering shifts result in long day and night changes. At any given time somewhere on Earth experiences longer nights than day or day longer than night. At the North Pole at night it can last for 24 hours and at the South Pole during the day can last for 24 hours. Vice versa.
Sun's circular shifts in a year and day and night changes as follows:
a. On 21 March to 23 September.
- The North Pole approaches the Sun, while the South Pole away from the Sun. The North Pole position is closest to the Sun on June 21st.
- The Northern Hemisphere receives more sunlight than the southern hemisphere.
- Length of day in the northern hemisphere is longer than in the southern hemisphere.
- The sun appears to shift northward until the north line is 23 ° 30 'LU when observed from the equator.
b. From 23 September to 21 March.
- The South Pole approaches the Sun, while the North Pole away from the Sun. The position of the South Pole is closest to the Sun on December 22.
- The Southern Hemisphere receives more sunlight than the Northern Hemisphere.
- Long day in the southern hemisphere longer than the northern hemisphere. Around the North Pole there are areas that experience the night 24 hours and around the South Pole there are areas that experience 24 hours a day.
- The sun appears to shift south to 23 ° 30 'LS when observed from the equator.
c. On 21 March and 23 September.
- The North and South Poles are equidistant from the Sun.
- The Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere receive as much sunlight.
- Length of day and night is the same length in all parts of the Earth.
- In the equatorial region, the Sun appears to pass directly above the head.
2. Solar Motion
The sun's position on Earth is not fixed, but it is shifting. The position of the Sun on the staircase1 December 22 to June 21 shifts northward to the northernmost line (GBU), which is 23 ° 30 'N latitude. Meanwhile, on the ladder1 June 21 - December 22 the position of the sun shifts southward to the southern return currents (GBS), latitude 23 ° 30 'LS. On the stairs1 March 21 and September 23 or the equator. The shift in the position of the Sun is called the Sun's daily pseudo motion. Actually the sun does not move, but the Earth is moving. The Earth's revolution with a sloping axis of rotation causes as if the position of the Sun is shifting. We can prove the existence of pseudo-motion of the Sun by observing the rising sun point. For example in this month the Sun rises on the hill. After a month, two months, or three months the rising point of the Sun must shift probably to the north or south of the hill.
3. Substitution Season
Sun's shifting shoreline resulted in changing seasons in tropical regions such as South Asia, Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, East Asia, and Northern Australia. In the tropics the seasons are distinguished into dry dry seasons and wet wet seasons. When the Sun is in the northern hemisphere (April-September), the Asian region experiences a dry season and the North Australian region experiences a rainy season. Conversely, when the Sun in the southern hemisphere (October-March), the area of North Australia is experiencing the dry season, and the Asian region experiencing the rainy season.
In subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere such as the United Kingdom, the United States, and Canada, as well as the southern hemisphere such as Australia and New Zealand, seasons are differentiated into spring, rainy season, summer, and fall. The types of seasons in the subtropics and the timing of occurrence are as follows:
a. Season in Northern Hemisphere:
- Spring: March 21-June 21
- Summer: June 21-September 23rd
- Autumn: September 23-December 22nd
- Winter: December 22-March 21st
b. Season in Southern Hemisphere:
- Spring: September 23 - December 22nd
- Summer: December 22 - March 21st
- Autumn: March 21st - June 22nd
- Winter: June 21 - September 23rd
That Means You've Been Helping Steemians Around The World Who Are Not Getting Enough Appreciation Or Support. So Come And Support...
>*"LITTLE FISH MUST HELP LITTLE FISH"*
Congratulations @aceh-trades! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Congratulations @aceh-trades! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!