| Español | English |
Enunciado
x + 1/x = √ 3 , |
|---|
Este tipo de problemas pertenecen al ámbito de las funciones simétricas y aunque es posible solucionarlos de una forma algebraica , vamos a seguir la senda del análisis combinatorio .
Preliminares
x = α , 1/x = β
-a1 = (1) = ∑ α = α + β = √ 3
a2 = (12 ) = ∑ α β = α ∙ β = 1
Nos facilitan los valores de las funciones simétricas elementales (1), (12).
Nos piden determinar el valor de la suma de potencias de índice 2024.
s2024 = (2024) = ∑α 2024 = α 2024 + β 2024
Desarrollo
La relación entre las funciones simétricas elementales y la suma de potencias es la razón de ser de las identidades de Newton ,
sn − a1sn-1 + a2sn-2 − ... + (−1)nnan = 0
Esta ecuación nos permite establecer una relación de recurrencia en sn
s1 = a1
...
sn = a1sn-1 − a2sn-2 + ... + (−1)n + 1nan
s1 = − √ 3
s2 = (− √ 3 ∙ − √ 3 ) − (2 ∙ 1) = 1
an = 0 , n > 2
sn+2 = − √ 3 ∙ sn+1 − sn
Hemos obtenido una recurrencia de orden dos, su ecuación característica determina el término general de la sucesión,
p2 + √ 3 p + 1 = 0
Con soluciones,
p = e ± i ∙5/6∙π
De la naturaleza de las soluciones de la ecuación característica inferimos que la sucesión es periódica,
5/6 ∙ n = 2k
5n = 12k
n = 12
∴ sn+12 = sn
sn+6 = -sn
Resolución
Solución
2024 ≡ 8 mod 12
s2024 = s8 = - s2
s2024 = - 1
∎
| English | Español |
Statement
x + 1/x = √ 3 , |
|---|
This is a problem on symmetric functions , solvable by pure algebraic methods, but here we are taking the combinatorial route and seeing...
Prelude
x = α , 1/x = β
-a1 = (1) = ∑ α = α + β = √ 3
a2 = (12 ) = ∑ α β = α ∙ β = 1
We know value of the elementary symmetric functions (1), (12).
We are asked for the value of the powers sum with 2024 index .
s2024 = (2024) = ∑α 2024 = α 2024 + β 2024
Development
Symmetric elementary functions related to powers sum ones by means of the Newtonian identities ,
sn − a1sn-1 + a2sn-2 − ... + (−1)nnan = 0
That is a recurrence relation on sn ,
s1 = a1
...
sn = a1sn-1 − a2sn-2 + ... + (−1)n + 1nan
s1 = − √ 3
s2 = (− √ 3 ∙ − √ 3 ) − (2 ∙ 1) = 1
an = 0 , n > 2
sn+2 = − √ 3 ∙ sn+1 − sn
We have a recurrence of second order, the general term is formed with solutions of its characteristic equation ,
p2 + √ 3 p + 1 = 0
p = e ± i ∙5/6∙π
We can infer that the sequence is periodic as the solutions of its charaterisitic equation .
5/6 ∙ n = 2k
5n = 12k
n = 12
∴ sn+12 = sn
sn+6 = -sn
Solution
Answer
2024 ≡ 8 mod 12
s2024 = s8 = - s2
s2024 = - 1
∎
Media
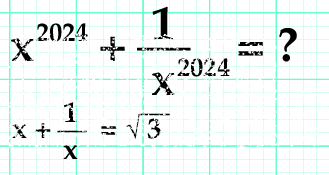
Congratulations @j2e2xae! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 400 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP