In this new week, we have a case of leukemia admitted and currently being managed by our team at the Haematology/Oncology unit of the Pediatrics department. So I am dedicating this post to discuss leukemia, the various types, risk factors, and treatment. Please stay on the line.
Manu Sharma, Scientific Annimations, CC BY-SA 4.0 Wikimedia
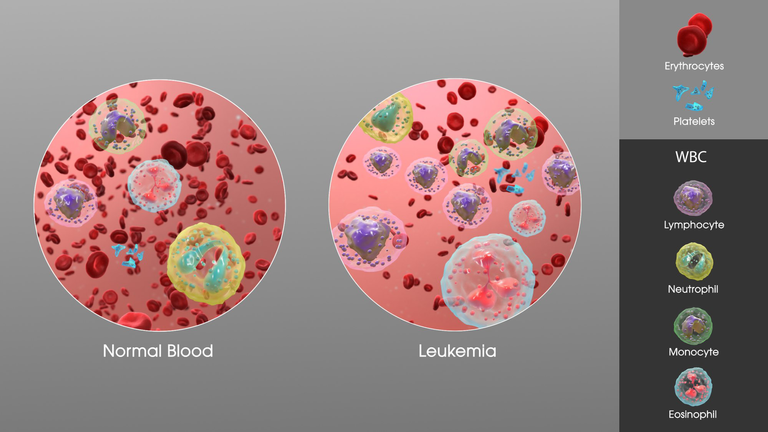
Leukaemia, commonly known as cancer of the blood is one of the childhood malignancies affecting the blood-forming tissues of the body. There are 3 blood types in the body. These are the red blood cells, white blood cells, and the platelets. They all perform very important functions in the body and when they are deficient in the body, a lot of problems start to come up.
The red blood cells in the body contain hemoglobin which transports oxygen to the tissues for the breakdown of the food we eat into energy (ATP) and heat. This energy is used by the body to drive the functions and activities of all other cells, tissues, and organs of the body including the brain, the heart, the liver, etc.
So, when the red blood cells are low (anemia), there is not enough oxygen to break down the food we eat to generate energy for the body's activities. The patient presents with weakness of the body, paleness, increased heart rate, etc. In severe cases, the organs of the body start to collapse, especially the heart. This is called anemia heart failure.
The white blood cells on the other hand help to fight off infections in our body. The environment of man is contaminated by microorganisms, including our skin, the air we breathe, the water we drink, our buccal mucosa, etc. But we don't get overwhelmed by the diseases caused by these microorganisms because we have the white blood cells in our body which help us to fight off these microorganisms.
In a situation where these white blood cells are low, our body will be left without any defense mechanism. The body will be like a government house without any army or police officer to defend it. The enemies can come in and have their field day without resistance. So in this case, the individual falls ill now and then because the microorganisms attack unopposed.
The 3rd blood cell is the platelets. These cells help in blood clothing. We notice that when you have a cut on the body, it bleeds and after a while, it stops because of the clothing factors. When these platelets are low in the body, the patient starts having some bleeding disorders and clotting problems.
Ibdipcan2015, CC BY-SA 4.0 Creative commons via Wikimedia
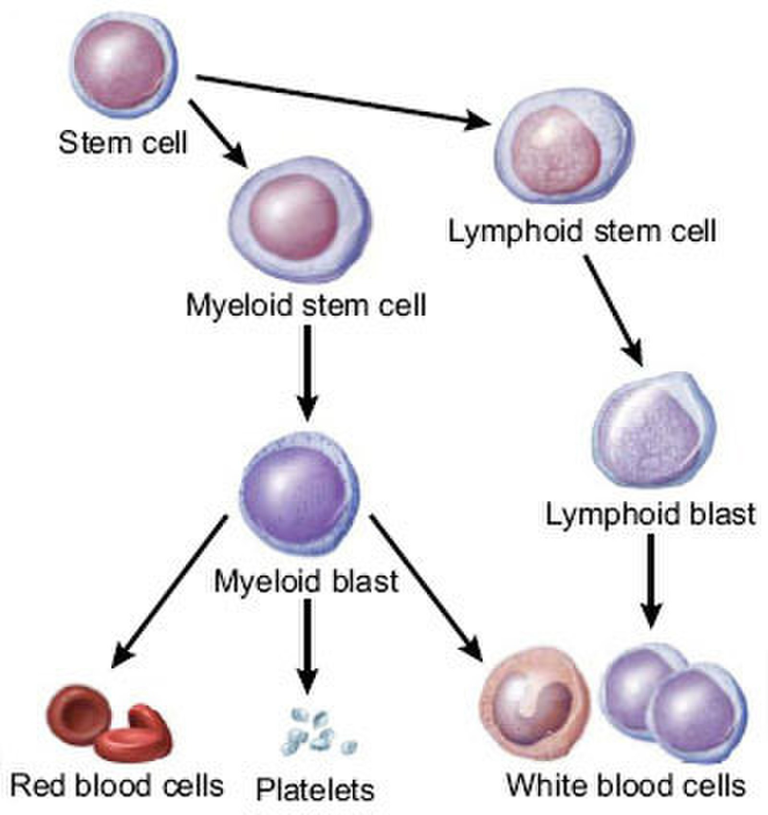
From the above discussion, we have seen how important these cells are to the body. These cells are produced majorly in the bone marrow and other organs of the body like the spleen and the liver.
Leukaemia is a malignant disease that affects primarily the white blood cells as well as the other cell lines. Cancer occurs when there is a genetic alteration in the DNA of cells. The cells start to proliferate and grow out of control. At the same time, the cells acquire a prolonged life span and don't die their natural death.
In leukemia, this uncontrolled production of abnormal white blood cells and the reduced rate of the natural cell death of these malignant cells cause a disruption of the normal function of the bone marrow which eventually leads to bone marrow failure.
CLINICAL FEATURES OF LEUKAEMIA
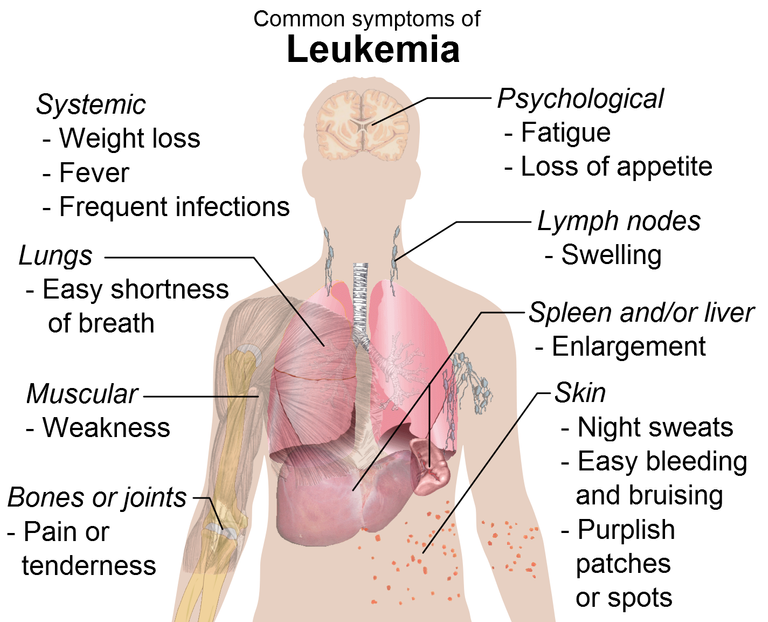
The clinical signs and symptoms of leukemia are that of the manifestation of bone marrow failure due to the uncontrollable proliferation of the blood-forming cells and their reduced cell death.
This bone marrow failure leads to low levels of the 3 cell types in the bone marrow; the red blood cells (anemia), the white blood cells (neutropenia), and platelets (thrombocytopenia).
So the patient presents with weakness and easy fatiguability due to the low red blood cells, recurrent infections, fever due to the low white blood cells, easy bruising, petechia, and mucosal bleeding due to the low platelets. These are the classical symptoms of leukemia and in most patients, there is a decrease in at least one or more cell lines.
Symptoms of leukemia usually manifest within 4 weeks of the onset of the disease and at first, the patient has a general feeling of unwell, loss of appetite, irritability, etc before the disease progresses to the symptoms of bone marrow failure described above.
Mikael Häggström, Public domain,
Wikimedia
In addition to the above symptoms, the malignant cells (leukemic cells) can infiltrate other parts of the body like the brain which causes neck stiffness, the bones and joints which causes bone and joint pain, the abdomen causing abdominal pain.
Other symptoms includes shortness of breath, difficulty in breathing due to the enlargement of the thymus.
TYPES OF LEUKEMIA
Leukemia affects primarily the white blood cells and can be either the lymphoid or the myeloid cells. There are four types of leukemia which are Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) which affect the lymphoid cells. Acute Myeloid leukemia (AML) and Chronic Myeloid leukemia (CML) which affect the myeloid cells. The acute leukemias occur rapidly over a short period of time while the chronic leukemias take a longer time to manifest.
The commonest type of leukemia seen in about 75% of the cases of leukemia is Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
THE PREVALENCE OF LEUKEMIA
According to pfizer,
Approximately 472,714 Americans have leukemia.
The American Cancer Society (ACS) predicts 60,650 new leukemia diagnoses in 2022 and roughly 24,000 deaths from the disease.
Among adults in the U.S., leukemia is the eleventh most common cancer, accounting for 3.2% of all new cancer diagnoses and 3.9% of all cancer deaths.
RISK FACTORS FOR LEUKAEMIA
The exact cause of leukemia is not known but some factors have been found to predispose individuals to this disease which includes both genetics and environment.
Some children have genetic inheritance/makeup which predisposes them to this disease. Some of these genetic factors include ataxia-telangiectasia, Fanconi anemia, trisomy 21, diamond black fan syndrome, etc. Twinning is also an important risk factor as the risk of a second twin developing the disease after the diagnosis in the first twin within one year of life is as high as 90 - 100%.
The environmental factors that predispose to leukemia include exposure to benzene, irradiation, alkylating agents, and certain viruses like the Epstein bar virus (EBV).
INVESTIGATIONS AND DIAGNOSIS OF LEUKAEMIA
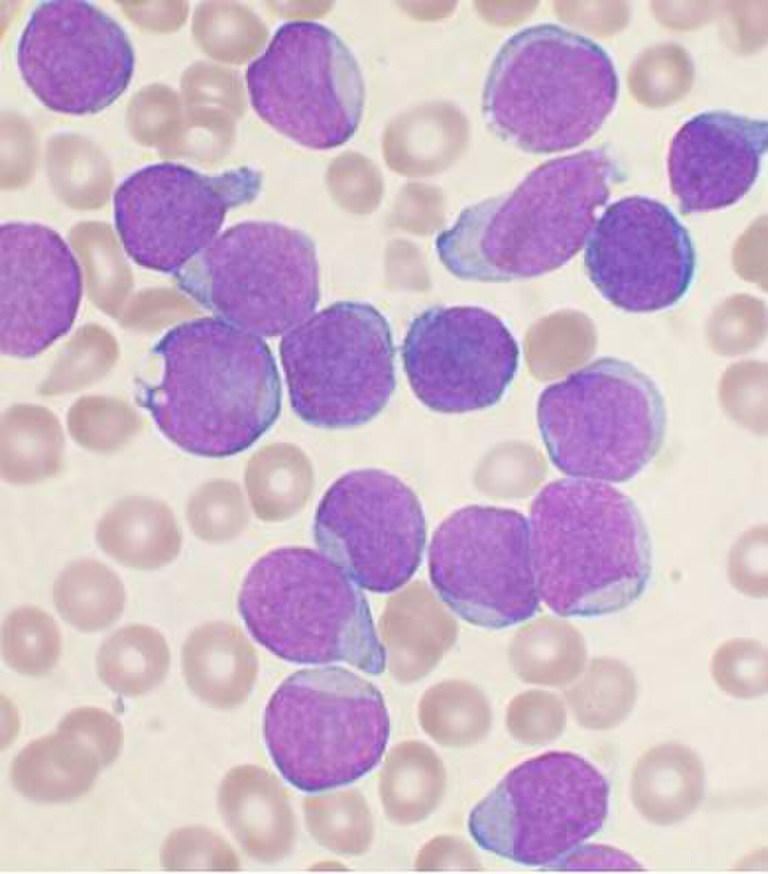
The relevant investigations in leukemia include a full blood count which shows reduced red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The white blood cells may be high due to the high rate of proliferation of the cells, but these cells are immature and cannot do the normal function of mature white blood cells.
By VashiDonsk at English Wikipedia., CC BY-SA 3.0 Creative commons via Wikimedia
A peripheral blood film is also done which shows the immature lymphocytes (blasts). This is used to confirm the diagnosis. A greater than 25 % of blasts in peripheral blood film confirms the diagnosis of ALL while a greater than 30% of blasts confirms the diagnosis of AML.
MANAGEMENT OF A LEUKAEMIA PATIENT
Managing a child with leukemia needs the utmost care and understanding of the disease. This is because the drugs commonly used to treat leukemia come with very strong side effects and care must be taken to avoid this.
Usually, before any course of chemotherapy is given, we usually request a full blood count of the patient to know if there will be a need to optimize the patient first before the therapy. Some of the patients usually receive a transfusion of red blood cells or platelets before the chemotherapy session.
The treatment of leukemia is in 3 phases, which include induction of remission, consolidation, and continuation. These are usually given at intervals to allow the cells to recover after each course before the next one.
A combination of chemotherapeutic agents commonly used includes; Cyclophosphamide, Prednisolone, Oncovin, Ara-C, Doxorubicin, Adriamycin, etc. Various regimens are used depending on the type of leukemia and the prognostic factors. These drugs help to kill cancer cells and have proven to be effective in the treatment of leukemia.
Other treatment options includes radiation therapy, stem cell transplant etc.
Supportive care is very important for this patient. Some of them have what we call tumor lysis syndrome. This results from the increased breakdown of tumor cells which pours their electrolytes into the circulation. This causes elevated potassium (hyperkalemia), uric acid (hyperuricemia), phosphate (hyperphosphatemia), and low calcium (hypocalcemia).
For patients who have this tumor lysis syndrome, we usually manage the patient with allopurinol, adequate hydration, and alkalinization of the urine. Other supportive care includes prophylactic antibiotics against some microorganisms and also adequate follow-up and examination of the testis for males and CNS as they may serve as the sanctuary sites for the cancer cells.
It is also very important that we adequately counsel and educate the patient, relatives, and caregivers on the cause, nature, and prognosis of the disease to incorporate them into the management process and allow them to understand the disease and take the right decisions because the treatment is usually for a very long period.
Fnaq, CC BY-SA 4.0 Creative commons, Wikimedia
The treatment outcome of leukemia can be good for patients who have good prognostic factors and most patients get the cure, however, some do relapse but the overall outlook is good except for those with bad prognostic factors.
Some good prognostic factors are patient age 1 to 9 years, lymphoid cell type, female sex, Caucasians, rapid response to therapy etc. While bad prognostic factors are ages less than 1 and above 10 years, non lymphoid cell types, male sex, blacks, slow response to therapy etc.
I hope that newer drugs and therapies in the nearby future will achieve a 100% cure for all forms of leukemia. And together, we will make every child with leukemia smile again.
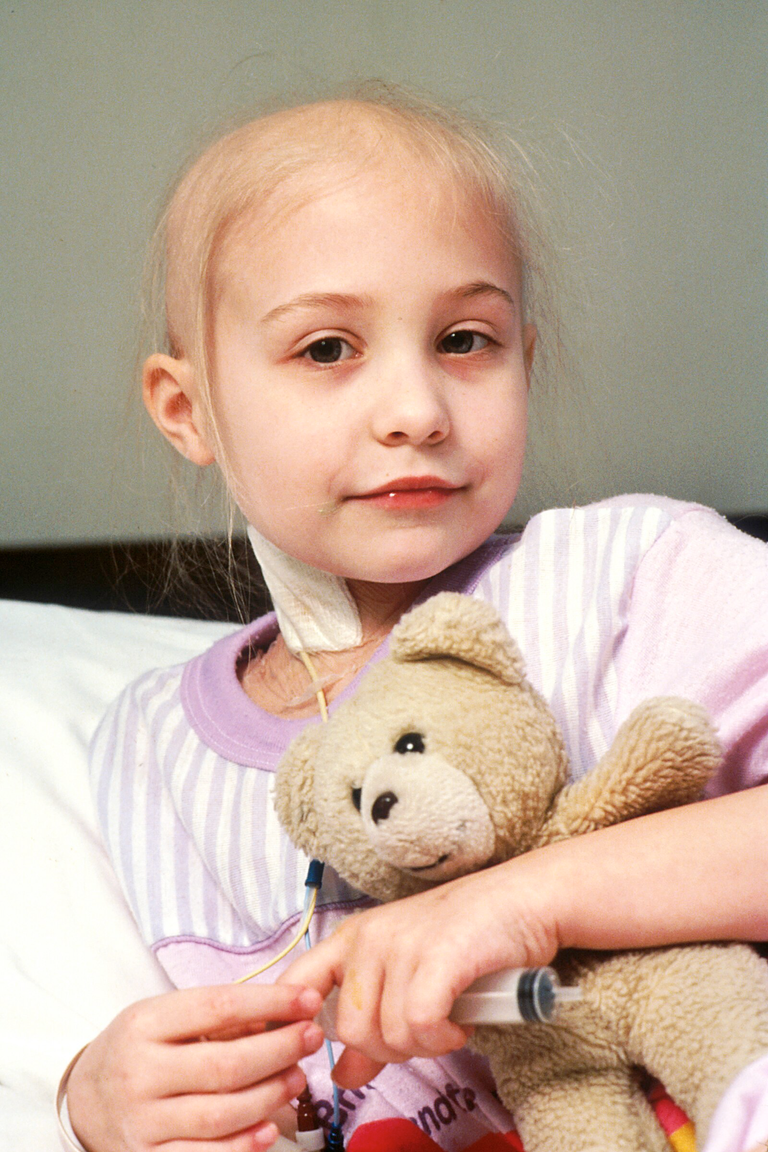
Bill Branson, Public domain, Wikimedia
Thanks so much for reading.
For references and further reading, please check the links below:
A patient with lukemia needs much love and support because it's a very depressing condition and so tiring to deal with.
Yes, you're absolutely correct!
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Thanks so much for your great support @stemsocial