Welcome readers, in this article we will discuss how a women's body changes and adapts itself during pregnancy. It's quite a remarkable ability of the body to adapt itself during this state. As we all know, a women's body undergoes a lot of transformation during the nine-month period. Some of the changes like weight gain, morning sickness, etc are easily noticeable and some changes are quite unexpected like fluid retention.
A nine-month pregnancy is divided into 3 trimesters. A normal pregnancy lasts for about 280 days or 40 weeks approximately. If a baby is born before 37 weeks, it's known as a preterm baby. The total weeks of pregnancy are calculated from the last day of the menstrual period to the birth of the baby. This total time frame is divided into 3 trimesters. First trimester, second trimester and third trimester. trimester just means a period of 3 months. The fetus and the body of the mother undergo tremendous changes during these trimesters. We will discuss, what are the changes and adaptions in the mother's body according to the trimesters. Let's get right into the topic now.
Changes in the First trimester (3 months or 12 weeks)
The first trimester starts from the last day of the menstrual period and ends on the 3rd month. This trimester is very crucial because it defines the fertility of the parents and makes the foundations of the healthy baby. Many important changes occur in the women's bodies that are easily noticeable. We can classify those changes as subjective and objective changes.
[By Caitlinamy, Wikimedia licensed under
CC BY-SA 4.0]
Since the weeks of pregnancy Are calculated from the last day of the menstrual period, technically, a woman is not pregnant in the first week. But might experience some mood swings. Ovulation occurs during the 2nd week. Ovulation means the release of the mature egg that is ready to be fertilized by a sperm. A woman might feel slight abdominal pain during this period. Also, an increase in body temperature is indicative of ovulation. The mature egg is fertilized by the sperm in 2nd week. In the 3rd week, the fertilized ovum implants itself in the lining of the uterus. At this point, a woman might experience implantation bleeding.
Subjective changes after implantation of fertilized ovum:
There are many subjective changes during the first trimester. Here is an overview.
week 2 - week 9
- Amenorrhea: Meaning the absence of normal menstruation. This is a universal symptom of pregnancy. If amenorrhea persists, then a couple must rule out conception. This is completely physiological and normal.
- Morning Sickness: It refers to nausea and vomiting and is common in 1st trimester of the pregnancy. starts at week 6 normally. It can be unpleasant sometimes and hamper day to day activity.
- Frequency of Micturition: The frequency of the micturition is noticeably increased during the late phase of 1st trimester. The main reason behind this is, large bulky uterus rests over the urinary bladder.
- Breast discomfort: A woman might feel pricking or fullness sensation in the breast, during the middle of the 1st trimester.
- Food cravings
Objective changes
Objective changes are the true physical changes that are noticeable by the woman and doctors. Here are some of those changes;
Week 10
Breast Changes: From week 10 onwards, major physical changes occur. The breast becomes more vascular. Prominent veins are visible over the breast. A thick yellowish secretion can also be expressed from 12 weeks onwards.
Week 11 to 12
Vaginal Changes: Walls generally become soft and a dusky hue is seen due to vascular congestion. This might start at the 8th week. Also, there is an increased pulsation.
Abdominal changes: Major changes in the belly are seen from the 11th week onwards. You might notice a baby bump, but at this point, the uterus still remains inside the pelvis. The baby bump might just be felt as a suprapubic bulge. The uterus is the size of a fetal head by the 12th week. Also, the shape becomes more globular.
Changes in the Second Trimester (4-6 month or 13 to 28 weeks)
Although the changes occurred in the 1st trimester is felt clearly by the mother, it might not be physically noticeable by other people. In the second trimester, changes are more clearly noticeable. We can see these changes as objective and subjective changes;
Subjective changes:
week 13 - 19
- Obviously, the amenorrhea continues: There is no menstruation, but the feeling of nausea and vomiting subsides. Also, the frequency of urination is decreased.
- Quickening: This means, the mother can actually feel the active fetal movements. It usually starts at around 18 weeks.
- Enlargement of the abdomen: Obviously, the belly is double to that of in the 1st trimester.
- Braxton hicks contractions; These are the irregular contractions felt by the mother. Also, these corrections are painless.
Objective Changes
Week 20 onwards
Breast changes: The breasts are further enlarged with more prominent veins. A variable degree of stria (lines) develops due to stretching of the breast.
Active fetal movements are palpated and external allotment can be elicited. Also, fetal heart sound is more appreciable around these weeks.
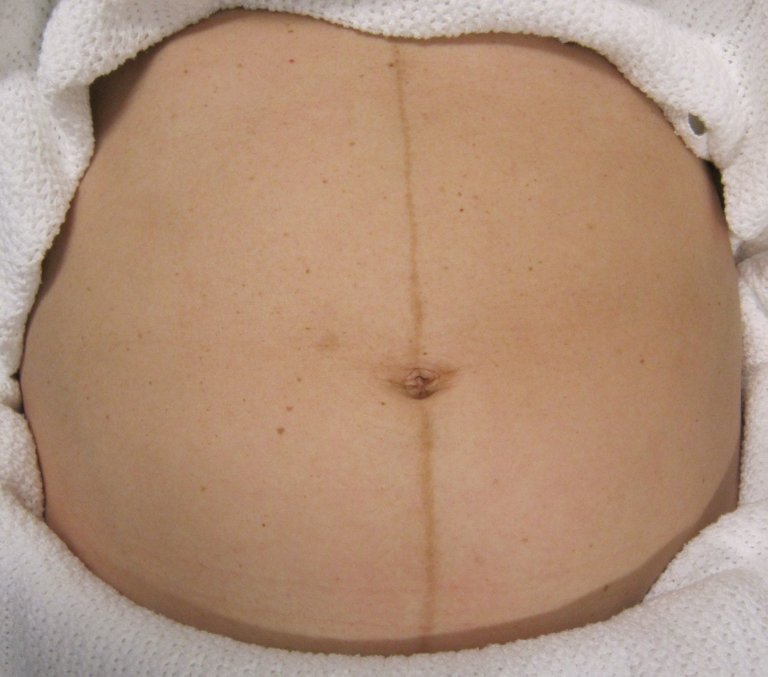
Abdominal changes: A pigmentation line is more visible from 20 weeks onwards which extends from the xiphoid process to the symphysis pubis. Also, many stria are seen on the abdomen due to stretching.
Skin changes: Varying degree of acne and pigmentation is seen on the forehead and cheeks.
Around 28 week
The fundal height is greatest at upper two-third and the lower one third between the xiphoid process and umbilicus. Braxton hicks contractions are now palpable with hands.
Changes in the third trimester (7-9 months or 28 to 40 weeks)
This is the last stage of pregnancy and a more vulnerable stage too. As changes occur, they become more evident.
Subjective changes:
- The amenorrhea obviously continues.
- No symptoms like nausea and vomiting are seen. If observed, they might be due to other reasons.n
- Lightning: This is the sense of relief that a mother feels around 38 weeks, when the presenting part of the baby, engages with the pelvis and diaphragm is released. Which makes breathing much easier for the mother.
- Frequency of urination; Since the baby defends down, it pushes the bladder, which in turn increases the frequency of micturition.
- More visible and pronounced active fetal movements are visible.
Objective changes;
More cutaneous changes are seen in this trimester. The skin around the abdomen becomes more pigmented, with varying numbers of lines due to massive stretching.
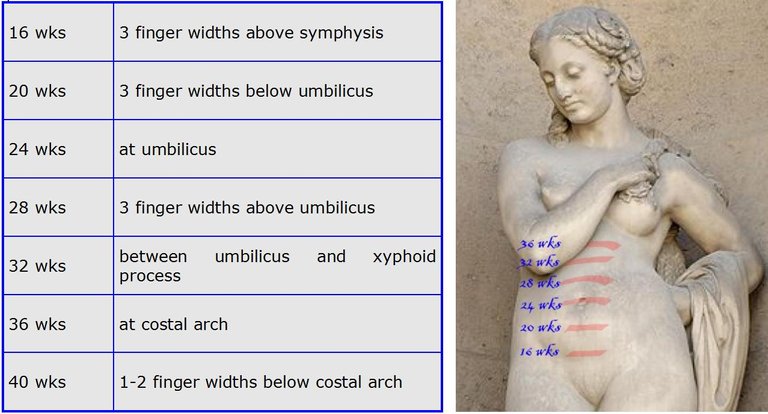
[Height of fetus in respective weeks by Ulysse2121, Wikimedia licensed underCC BY-SA 3.0]
Abdominal changes: the shape of the uterus becomes spherical beyond 36 weeks. The fundal height reaches up to the xiphoid process by 36 weeks and again descents because, its time for delivery. The contractions are now easily palpable and fetal movements are felt easier than before.
These were the normal changes that happen in a mother's body. Now, we will see how the different systems of the body adapt to these changes. We will have an overview according to the different systems.
Adaptations in the body during pregnancy
Cutaneous adaptation:
We can see excess pigmentation on the forehead, cheeks, and around the eyes. This phenomenon is known as Chloasma gravidarum or pregnancy mask. This can be patchy or diffuse in nature.i
Excess brown lines: The formation of brownish lines from the xiphoid cartilage to the symphysis pubis is clearly visible. This adaptation is due to the formation of excess melanocytes and stretching in that region.
Stira gravidarum: These are depressed linear lines developed in the walls of the abdomen clearly visible from outside and are present mostly below the umbilicus, over thighs, and breasts. After the delivery, they turn white and are called stria Albicans.
Weight gain
Of course, there is a huge amount of weight gain during pregnancy. There is an average weight gain of 11kgs. 1kg in the first trimester, and 5 kgs each in the 2nd and 3rd trimester.
The reproductive weight gain is about 6 kgs, which means the total weight of the fetus, placenta, fluids, and uterus.
The real maternal weight gain is about 5 kgs, which includes, increase in blood volume, extracellular fluids, fats, and proteins.
Body Fluid adaptaitons
A large volume of fluid is retained during the pregnancy. It is about 6.5 liters out of which 3.5 L contributes to amniotic fluid, fetus, and placenta. Since the fluid is in large amounts, this state is known as hypervolemia. Also, a large amount of sodium and potassium ions are also retained in the body. The causes for this are mentioned below;
- There is a change in osmoregulation which interferes with fluid metabolism.
- Pregnancy produces more estrogen and progesterone.
- Increase in renin-angiotensin activity, which in turn helps in reabsorption of water and ions.
- Increse in aldosterone.
Hematological system
In pregnancy, the body demands more blood to complete its daily activities and for well being of the fetus. Therefore, the blood volume starts to increase after the 7th week and reaches 35-45 % above the normal level. This increase is about 1500 ml of extra blood.
Plasma volume also starts rising after 7th week and reaches up to 45-50 % of the normal level. This increase is about 1250 ml of extra plasma.
Also, the Mass of red blood cells (RBC) increases by 20% which is needed to fulfill the oxygen demand. Although, RBC is increased but mother can still be in the state of anemia. This is because of a more increase in plasma volume which dilutes the RBC.
Cardiovascular system
This refers to the heart and blood vessels. The heart is generally pushed upwards and outwards. The reason behind this is the elevation of the diaphragm by the enlarging uterus. The heartbeat or apex beat which is audible in 5th intercostal space in a normal person is shifted to 4th intercostal space. Pulse is also slightly increased.
Although there is increase in blood volume, blood pressure is seen to be decreased in most cases. This is because there is fall in the vascular resistance of the blood vessels.
Respiratory system
A mother can sometimes feel breathless. As the diaphragm is pushed upwards about 4cm which reduces the lung capacity. This is called diaphragmatic breathing. The chest expands by more than 2 cm while breathing and circumference are increased by 5-7 cm.
A period of hyperventilation might occur, which causes a fall in Co2 pressure and an increase in Oxygen pressure, which results in respiratory alkalosis.
Gastrointestinal system
The gums become congested with blood vessels and very spongy. Hence, small injury to the gums can cause heavy bleeding from the mouth. Also, the muscle tone and motility of the GI tract are reduced which sometimes can lead to constipation. The gastric sphincter is also relaxed in pregnancy which causes regurgitation of the food leading to vomiting and heartburn. Reduces motility of the tract leads to delayed stomach emptying leading to anorexia.
Nervous system
Minor temperature changes are very common during pregnancy. Mental irritability and lack of sleep are also commonly seen. Sometimes, a mother might experience psychosis and depression.
Sometimes, the median nerve in the wrist, under the flexor compartment is also compressed leading to carpal tunnel syndrome. It starts with a tingling sensation in the fingers.
Might experience loss of sensation in the thigh also known as parenthesis, due to compression of a lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh
That's it for this article readers, see you in the next one
I hope you liked it.
*All images used are copyright free and are provided with appropriate credits*
References:
https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/bodily-changes-during
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maternal_physiological_changes_in_pregnancy
https://www.parents.com/pregnancy/signs/symptoms/a-pregnancy-symptom-timeline/
https://www.livescience.com/50877-regnancy-body-changes.html
https://familydoctor.org/changes-in-your-body-during-pregnancy-first-trimester/

@tipu curate 3
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 0/4)
Congratulations @idoctor! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your board And compare to others on the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
!discovery 30
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our community! hive-193212
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support. Using the STEMsocial app could yield even more supporti next time.