With this new format I want to make it easier for interested readers to get a broader overview of exciting current research results. Based on my own background and profession, I will focus primarily on the scientific fields of:
- Chemistry
- Physics and
- Molecular biology
For this I will present selected, recent, scientific work in short form. If someone comes across a topic that he is particularly interested in, do not hesitate to satisfy your thirst for knowledge and use the References, which I will provide for every topic, to get a deeper insight. :)
Scientific News #1
Topic 1: Laboratory layered latte
Double diffusive convection is a fluid dynamics phenomenon and is both the principial and also the quantitative basis for the work published by Xue and co-workers in Nature Communications. (see Reference) It is known, that the introduction of thermal gradients in fluid systems with initial, well-defined density gradients results in the formation of differentiable layers. But also starting from a chaotic initial state such structured states with distinct layers can be achieved.
First, they present their experiment in which warm coffee is introduced into warm milk and show that stratification occurs within minutes, using two miscible liquid phases and adjusted injection rates. For a movie of their initial experiment click here or look it up in the reference. The findings obtained from the more detailed investigations were used to provide the application-oriented material science with a new single-step process to produce layered structures in soft materials, where the local elastic properties vary step-wise along the length of the material.
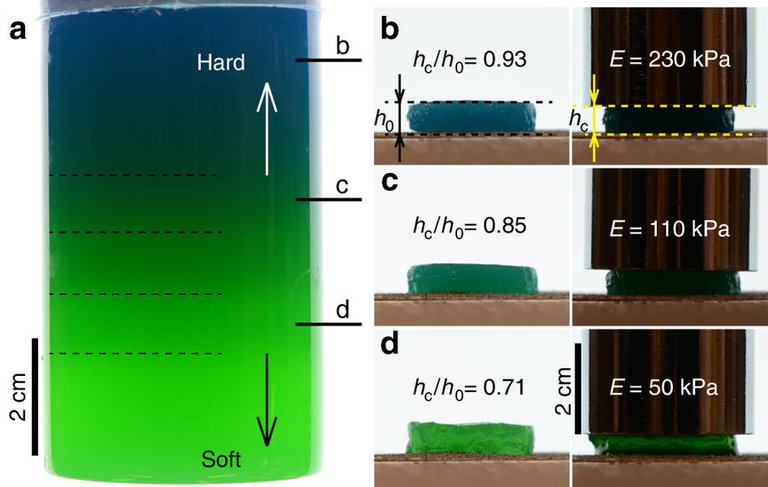
The image above shows their result of a single-step fabricated soft layered gel. This was achieved by injecting a 4 wt-% agarose solution with 0.0015 wt-% methylene blue hydrate into a 9.1 wt-% solution of sodium chloride containing 0.002 wt-% fluorescein sodium salt. In a the color gradient reflects also the distribution of agarose inside the rod, with gives rise to differing softness in different layers: i.e. bottom layers are softer than those at the top. In b - d the different mechanical properties of cylindrical gel slaps, which were cut from different layers in the gel, are shown.
The truly amazing part of her work lies in the quantitative analysis and consideration of the underlying phenomena in this process.
Reference:
N. Xue, S. Khodaparast, et.al: Laboratory layered latte, Nature Communications, 2017, 8, 1960
Topic 2: Deep-learning methods for drug discovery
New multi-layered neural networks have improved speech recognition and machine vision, and can be trained to make predictions for life sciences and materials science. They can also be used for the prediction of protein-ligand interactions and for electronic properties of molecular materials. The prerequisites for this are that enough reference data points are available for the learning process. Altae-Tran and co-workers have now shown how iterative one-shot learning can be used to solve this problem.
Developed on the basis of the Deepchemsoftware, their method predicts the bioactivity of substances based on as few as some thousand reference data points! Accordingly, also the work of Goh and co-workers shall be mentioned. They give an overview of the use of deep learning in computational chemistry.
Reference:
H Altae-Tran, et al: Low Data Drug Discovery With One-Shot Learning, ACS Cent Sci. 2017, 3 (4), 283-293.
Garrett B. Goh, et.al: Deep learning for computational chemistry. J. Comput. Chem.. 2017, 39, 1291-1307.
Topic 3: Photoluminescent uranyl organic framework
Until recently the detection limit for chemical dosimeters used to be 0.007 Gray. But now Xie and co-workers have synthesized a MOF (metal organic framework) from uranyl nitrate, oxalic acid, succinic acid, and tetramethylammonium bromide. The resulting green crystals show a photoluminescence whose strength decreases quantitatively with the applied radiation dose.
.jpg)
generic green crystals - Image Source
When exposed to X-ray or gamma irradiation, radicals are formed in the MOF. These radicals are then stabilized by the oxalate-carboxylate structure and quench the luminescence. The method improves the detection limit for radiation doses by two orders of magnitude compared to solvent-based photoluminescence dosimetry. Hence the new DL is roughly 0.0001 Gray! The radicals are stable for at least six hours, and twelve hours of heating fully recovers the quenched photoluminescence.
The ability to measure relatively low X-ray or gamma doses is important in a broad variety of fields spanning medicine, radioprotection and the investigation of cosmic radiation.
Reference:
J. Xie, Y. Wang, et.al: Highly Sensitive Detection of Ionizing Radiations by a Photoluminescent Uranyl Organic Framework, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7500.
Economic-scientific Note: Mining in space
Luxembourg is the first European country to regulate the mining of mineral resources on asteroids and other celestial bodies. The US passed a similar law in 2015. The regulations of Luxembourg refer to the ownership of materials mined in space and are initially valid for space travel and a New Space Industry. In space, experts suspect a potential for billions of dollars in raw materials. For example, asteroids have high concentrations of metals such as platinum and rare earths.
The intention behind this law is to regulate the extraction of valuable raw materials from space bodies and to draw companies to Luxembourg. There's even a $ 230 million fund to get companies to build their space-mining businesses in Luxembourg!
Reference:
M. Kaufmann: Luxembourg's Asteroid Mining is Legal Says Space Law Expert, Inverse Innovation, 1st Aug. 2017
I hope you liked the first edition of my new format.
If you want to see more of these articles, follow me!
Best,
mountain.phil28




Nice work...but I'm already following you^^
Haha that's not a problem. Also you are invited to enjoy some scientific news. 😎
I like the idea of doing a short, science news post series. However I find having all of your text centered, makes things a bit harder for me to read then it would be otherwise.
Cheers.
Thanks for your commen! I will consider this in my next Scientific News article. ;)
Best,
mountain.phil28
Well thoughtout intro BUZZme already all up in your blog ;) ha ha
topic1>You hade me at coffee ;)
1>new> 'layered structures', which was what? well picket pictures for this one :D
2>woow cool wanT more on this one :D
3> me lost at>oxalate-carboxylate structure and quench the luminescence. LOL
They are actually stable for that long??? wow :D
4> I hope you are going to talk roockis metal &asteroids noot cash ;0
I like your lay out :D :D well done sweetness :D💜
Thanks for the compliments. :)
1> That's the reason I choosed this topic. :D
4> I guess everything that is mined can somehow turned into cash.^^
Thanks again. Your support means a lot to me! :)
Best,
mountain.phil28
😍A very informative post. Great job. Keep it up! 😍

😍 Çok bilgilendirici bir yazı. İyi iş. Aynen böyle devam! 😍