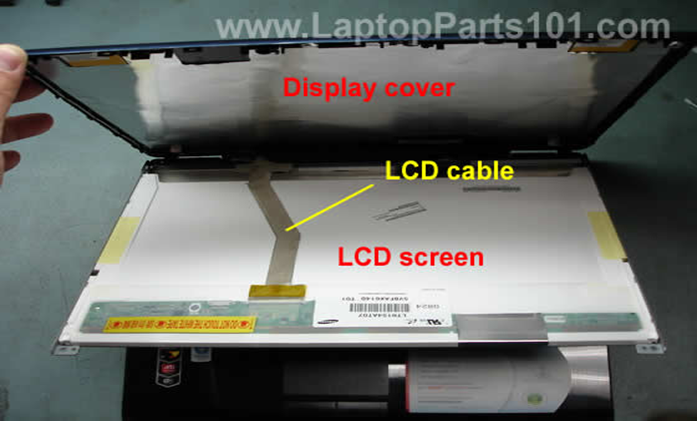
The main output device for a microcomputer is display. It is often a flat plane device known as Liquid Crystal Display(LCD).
This display monitor is similar to a TV ,but designed to be viewed at much higher rates, typically more than 72 frames per second.
The PC systems today use 14.1",15.6",17"display. Larger display is available but are very costly.
At present PC display are able to display images with pixel resolutions.
There is some range like 1280×720.This means horizontal 720 line where each line contain 1024 picture elements or
pixels.

Pixel is the smallest picture element that can
be created and displayed by the display monitor.
- Polarizing filter film with a vertical axis to polarize light as it enters.
- Glass substrate with ITO electrodes. The shapes of these electrodes will determine the shapes that will appear when the LCD is switched ON. Vertical ridges etched on the surface are smooth.
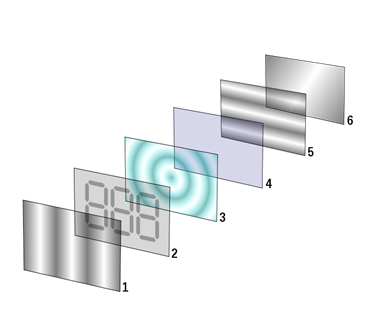
- Twisted nematic liquid crystal.
- Glass substrate with common electrode film (ITO) with horizontal ridges to line up with the horizontal filter.
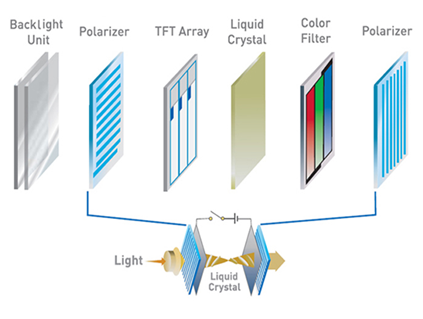
- Polarizing filter film with a horizontal axis to block/pass light.
- Reflective surface to send light back to viewer. (In a backlit LCD, this layer is replaced or complemented with a light source.)
Advantages:
- Low power consumption.
- Low cost.
- Small size.
Disadvantages:
- LCD’s do not emit light, as a result, the image has very little contrast.
- Screen is susceptible to glare, so the optimum viewing angle is narrow.
- LCD’s have less color capability.
- Resolution is not as good as that of CRT
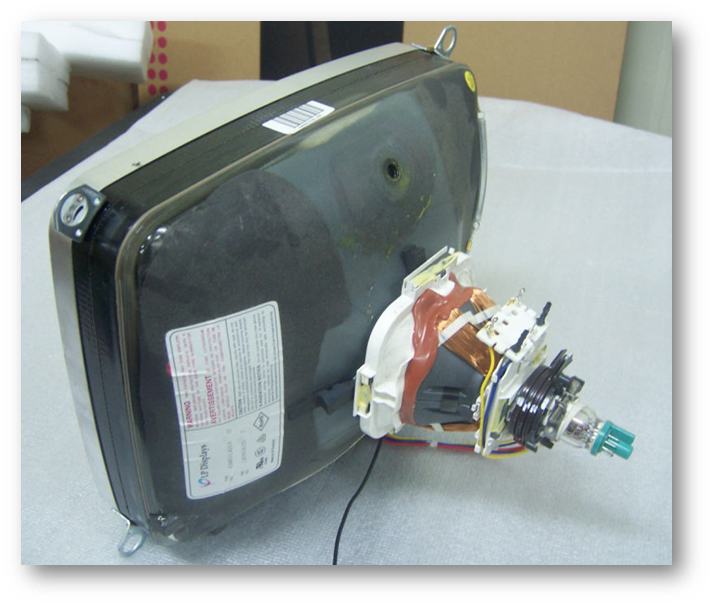
The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube that contains one or more electron guns and a phosphorescent screen, and is used to display images. The display was used before.